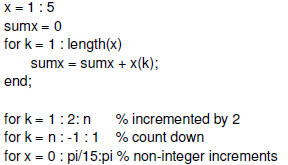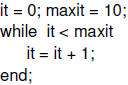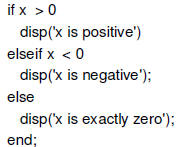MATLAB Primer
Control Flow • The control-flow statements of a programming language specify the order in which computations are performed. |
For Loop
|
While Loop • When an iteration is repeated until some termination criterion is met.
• Other ways to exit from a loop construct |
Condition Execution
|
Switch Construct
|
Function • Functions break large computing tasks into smaller ones, and enable people to build on what others have done instead of starting over from scratch. • Appropriate functions hide details of operation from part of the program that don’t need to know about them. |
• Use local variables that exist only while the function is executing. Local variables are distinct from variables of the same names in the workspace. • Function files are reusable. • Specific tasks can be encapsulated into functions. This modular approach enables development of structured solutions to complex problems. |
• Function [argouts] = funName(argins) Variable numbers of input /pout parameters • Each function has internal variables, nargin and nargout can find how many input/output arguments. • Allow a single function to perform multiple related tasks. • All functions assume default values for some inputs, thereby simplifying the use of the function for some tasks. |
function [a, b] = myfun(x,y) % this function does % input variables: % x …… % y …… %output variables % a …… % b …… |
A Case Study • Problem: Building a simulation program which will receive the same input like human subjects and do the same test. • Main structure
|
Programming Styles • Programming style varies from programmer to programmer. It is good to stick to common coding practices. • A consistent programming style gives your programs a visual familiarity that helps the reader quickly comprehend the intention of the code. • A programming style consists of - visual appearance - conventions used for variable names - documentation with comment statements |
• Indent switch and loop blocks • Use meaningful variable names • In- line comments % |
• The best way is to assemble a whole program from well designed small functions. This will enhances readability and testing. • A function interacts with other code through input and output arguments and global variables. The use of arguments is almost always clearer than the use of globals. • Any block of code appearing in more than one m-file should be considered for packaging as function. |
• Each function can just do one task and should occupy roughly one screen. If your function is much longer, then you may want to consider to splitting it into two or more separate functions. • Every 5-10 lines of code should be accompanied by comments. However, commenting trivial operations such as incrementing of index variables is not necessary . |
| Prev | Next |